|
|
||
|---|---|---|
| .github | ||
| docker | ||
| examples | ||
| lerobot | ||
| media | ||
| tests | ||
| .dockerignore | ||
| .gitattributes | ||
| .gitignore | ||
| .pre-commit-config.yaml | ||
| CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md | ||
| CONTRIBUTING.md | ||
| LICENSE | ||
| Makefile | ||
| README.md | ||
| poetry.lock | ||
| pyproject.toml | ||
README.md

State-of-the-art Machine Learning for real-world robotics
🤗 LeRobot aims to provide models, datasets, and tools for real-world robotics in PyTorch. The goal is to lower the barrier to entry to robotics so that everyone can contribute and benefit from sharing datasets and pretrained models.
🤗 LeRobot contains state-of-the-art approaches that have been shown to transfer to the real-world with a focus on imitation learning and reinforcement learning.
🤗 LeRobot already provides a set of pretrained models, datasets with human collected demonstrations, and simulated environments so that everyone can get started. In the coming weeks, the plan is to add more and more support for real-world robotics on the most affordable and capable robots out there.
🤗 LeRobot hosts pretrained models and datasets on this Hugging Face community page: huggingface.co/lerobot
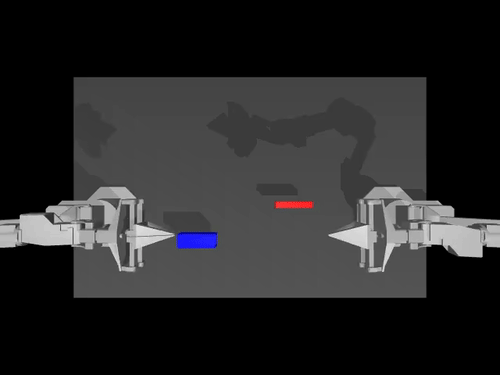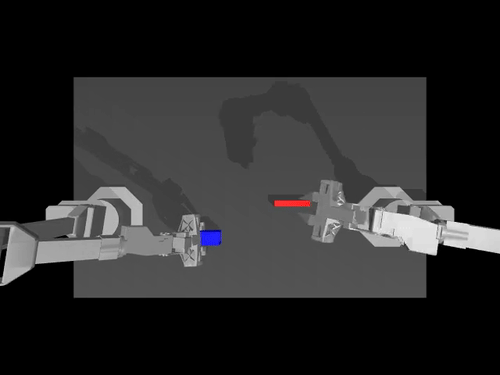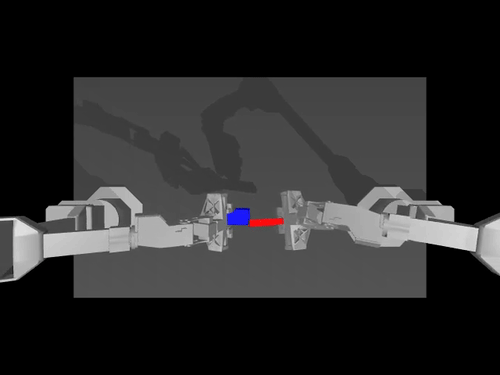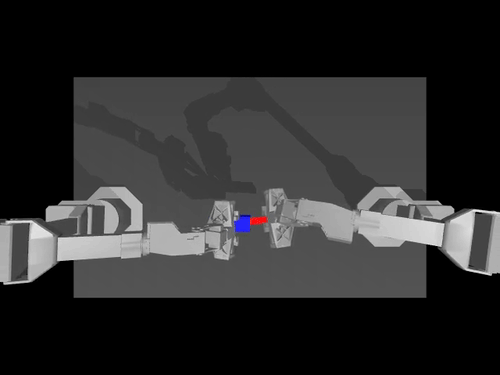
Examples of pretrained models and environments
 |
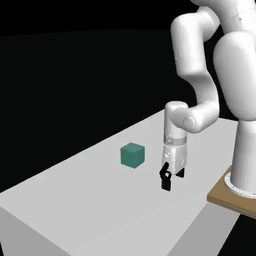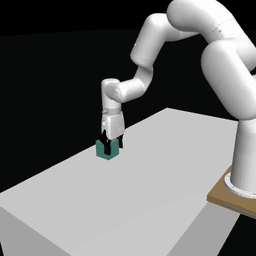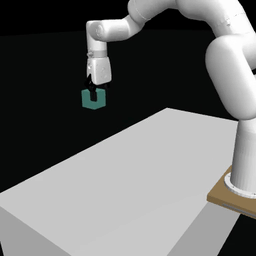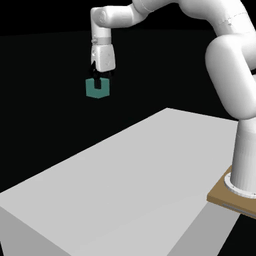 |
 |
| ACT policy on ALOHA env | TDMPC policy on SimXArm env | Diffusion policy on PushT env |
Acknowledgment
- ACT policy and ALOHA environment are adapted from ALOHA
- Diffusion policy and Pusht environment are adapted from Diffusion Policy
- TDMPC policy and Simxarm environment are adapted from FOWM
- Abstractions and utilities for Reinforcement Learning come from TorchRL
Installation
Download our source code:
git clone https://github.com/huggingface/lerobot.git && cd lerobot
Create a virtual environment with Python 3.10 and activate it, e.g. with miniconda:
conda create -y -n lerobot python=3.10 && conda activate lerobot
Install 🤗 LeRobot:
pip install .
For simulations, 🤗 LeRobot comes with gymnasium environments that can be installed as extras:
For instance, to install 🤗 LeRobot with aloha and pusht, use:
pip install ".[aloha, pusht]"
To use Weights and Biases for experiment tracking, log in with
wandb login
Walkthrough
.
├── examples # contains demonstration examples, start here to learn about LeRobot
├── lerobot
| ├── configs # contains hydra yaml files with all options that you can override in the command line
| | ├── default.yaml # selected by default, it loads pusht environment and diffusion policy
| | ├── env # various sim environments and their datasets: aloha.yaml, pusht.yaml, xarm.yaml
| | └── policy # various policies: act.yaml, diffusion.yaml, tdmpc.yaml
| ├── common # contains classes and utilities
| | ├── datasets # various datasets of human demonstrations: aloha, pusht, xarm
| | ├── envs # various sim environments: aloha, pusht, xarm
| | ├── policies # various policies: act, diffusion, tdmpc
| | └── utils # various utilities
| └── scripts # contains functions to execute via command line
| ├── eval.py # load policy and evaluate it on an environment
| ├── train.py # train a policy via imitation learning and/or reinforcement learning
| ├── push_dataset_to_hub.py # convert your dataset into LeRobot dataset format and upload it to the Hugging Face hub
| └── visualize_dataset.py # load a dataset and render its demonstrations
├── outputs # contains results of scripts execution: logs, videos, model checkpoints
└── tests # contains pytest utilities for continuous integration
Visualize datasets
Check out example 1 that illustrates how to use our dataset class which automatically download data from the Hugging Face hub.
You can also locally visualize episodes from a dataset by executing our script from the command line:
python lerobot/scripts/visualize_dataset.py \
--repo-id lerobot/pusht \
--episode-index 0
It will open rerun.io and display the camera streams, robot states and actions.
Our script can also visualize datasets stored on a distant server. See python lerobot/scripts/visualize_dataset.py --help for more instructions.
Evaluate a pretrained policy
Check out example 2 that illustrates how to download a pretrained policy from Hugging Face hub, and run an evaluation on its corresponding environment.
We also provide a more capable script to parallelize the evaluation over multiple environments during the same rollout. Here is an example with a pretrained model hosted on lerobot/diffusion_pusht:
python lerobot/scripts/eval.py \
-p lerobot/diffusion_pusht \
eval.n_episodes=10 \
eval.batch_size=10
Note: After training your own policy, you can re-evaluate the checkpoints with:
python lerobot/scripts/eval.py \
-p PATH/TO/TRAIN/OUTPUT/FOLDER
See python lerobot/scripts/eval.py --help for more instructions.
Train your own policy
Check out example 3 that illustrates how to start training a model.
In general, you can use our training script to easily train any policy. To use wandb for logging training and evaluation curves, make sure you ran wandb login. Here is an example of training the ACT policy on trajectories collected by humans on the Aloha simulation environment for the insertion task:
python lerobot/scripts/train.py \
policy=act \
env=aloha \
env.task=AlohaInsertion-v0 \
dataset_repo_id=lerobot/aloha_sim_insertion_human \
hydra.run.dir=outputs/train/aloha_act
Here is an example of logs from wandb:

You can deactivate wandb by adding these arguments to the command line:
wandb.disable_artifact=true \
wandb.enable=false
Note: During training, every checkpoint is evaluated on a low number of episodes for efficiency. After training, you may want to re-evaluate your best checkpoints on more episodes or change the evaluation settings. See python lerobot/scripts/eval.py --help for more instructions.
Contribute
If you would like to contribute to 🤗 LeRobot, please check out our contribution guide.
Add a new dataset
To add a dataset to the hub, begin by logging in with a token that has write access, which can be generated from the Hugging Face settings:
huggingface-cli login --token ${HUGGINGFACE_TOKEN} --add-to-git-credential
Then move your dataset folder in data directory (e.g. data/aloha_ping_pong), and push your dataset to the hub using the following command:
python lerobot/scripts/push_dataset_to_hub.py \
--data-dir data \
--dataset-id aloha_ping_ping \
--raw-format aloha_hdf5 \
--community-id lerobot
See python lerobot/scripts/push_dataset_to_hub.py --help for more instructions.
If your dataset format is not supported, implement your own in lerobot/common/datasets/push_dataset_to_hub/${raw_format}_format.py by copying examples like pusht_zarr, umi_zarr, aloha_hdf5, or xarm_pkl.
Add a pretrained policy
# TODO(rcadene, alexander-soare): rewrite this section
Once you have trained a policy you may upload it to the Hugging Face hub.
Firstly, make sure you have a model repository set up on the hub. The hub ID looks like HF_USER/REPO_NAME.
Secondly, assuming you have trained a policy, you need the following (which should all be in any of the subdirectories of checkpoints in your training output folder, if you've used the LeRobot training script):
config.json: A serialized version of the policy configuration (following the policy's dataclass config).model.safetensors: Thetorch.nn.Moduleparameters, saved in Hugging Face Safetensors format.config.yaml: This is the consolidated Hydra training configuration containing the policy, environment, and dataset configs. The policy configuration should matchconfig.jsonexactly. The environment config is useful for anyone who wants to evaluate your policy. The dataset config just serves as a paper trail for reproducibility.
To upload these to the hub, run the following with a desired revision ID.
huggingface-cli upload $HUB_ID PATH/TO/OUTPUT/DIR --revision $REVISION_ID
If you want this to be the default revision also run the following (don't worry, it won't upload the files again; it will just adjust the file pointers):
huggingface-cli upload $HUB_ID PATH/TO/OUTPUT/DIR
See eval.py for an example of how a user may use your policy.
Improve your code with profiling
An example of a code snippet to profile the evaluation of a policy:
from torch.profiler import profile, record_function, ProfilerActivity
def trace_handler(prof):
prof.export_chrome_trace(f"tmp/trace_schedule_{prof.step_num}.json")
with profile(
activities=[ProfilerActivity.CPU, ProfilerActivity.CUDA],
schedule=torch.profiler.schedule(
wait=2,
warmup=2,
active=3,
),
on_trace_ready=trace_handler
) as prof:
with record_function("eval_policy"):
for i in range(num_episodes):
prof.step()
# insert code to profile, potentially whole body of eval_policy function





